Chromium-6 in Tap Water – The ‘Erin Brockovich’ Chemical
You may recognize the chemical Chromium-6 from the film that won Julia Roberts an Oscar. She portrayed Erin Brokovich, the titular character who uncovered Pacific Gas & Electric’s poisoning of the water supply in Hinkley, California for more 30 years.
Unfortunately, this chemical hasn’t gone away. We’re looking at the dangers of Chromium-6 and how you can protect your family from it.

What is Chromium-6?
In trace amounts, chromium is an essential part of the human diet. It helps regulate blood sugar, raises HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels in the blood, may help prevent heart disease, and can even combat depression.
Chromium in its beneficial form (trivalent chromium, or chromium-3) occurs naturally in the environment. You can get it by eating broccoli, grape juice, many meats, brewer’s yeast, onions, tomatoes, or in supplement form at your local health food store.
But there is another kind of chromium whose effect on the human body can be devastating. Hexavalent chromium, or chromium-6, is classified as a toxic heavy metal.
It is far more readily absorbed than chromium-3 and thus far more likely to reach toxic levels in the body. Chromium-6 has been linked to skin irritation; ulcers; respiratory problems; sperm damage; kidney damage; and cancer of the stomach, intestinal tract and lungs.
Historically, attention to chromium-6 toxicity has focused mainly on exposure suffered by workers in facilities that use chromium for industrial purposes. Of these cases, the majority involve inhalation of the chemical. However, hexavalent chromium can also contaminate water supplies. And an Environmental Working Group (EWG) report reveals that water-borne chromium contamination is far more common than anyone might have guessed.
How Does Chromium Get Into Tap Water?
Trace amounts of hexavalent chromium occur naturally in the environment in many areas. However, most incidents of high chromium levels in water can be traced to industrial sources.
The 2000 film Erin Brockovich told the true story of an environmental advocate who successfully sued the Pacific Gas and Electric Company for contaminating her community’s groundwater with chromium. Other industries that use chromium include leather tanning, stainless steel manufacturing, electroplating, textile production, and other manufacturing. The chemical commonly leaves factories as airborne particulate and eventually ends up in surface and ground water.
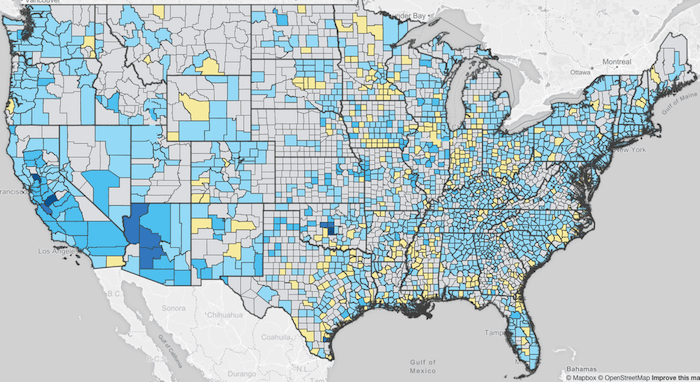
EWG reports that counties in every state in the continental U.S. have water supplies in which chromium levels exceed the .02 parts per billion that California scientists consider to be an acceptable limit for public health. In fact, over 3 out of 4 water samples in a nationwide EPA survey of over 60,000 samples were found to contain chromium levels at least this high. This is thought to affect over 218 million Americans.
Studies have also revealed high levels of chromium-6 in Canadian water supplies. Data compiled by Carex Canada suggests that elevated chromium-6 levels in drinking water may be contributing to an increase in cancer in the Canadian population.
Chromium Toxicity Affects Many People
In the case of oral ingestion, stomach acid plays an important role in breaking chromium-6 down into chromium-3 in the process of detoxification. Therefore antacid users, people with ulcers, and people with conditions associated with low stomach acidity such as pernicious anemia, pancreatic tumors and certain autoimmune diseases are more vulnerable to chromium toxicity.
No studies have been done regarding chromium toxicity in children. However, children, babies and fetuses are more sensitive to carcinogens in general.
Animal studies have shown adverse effects in developing fetuses related to high chromium exposure in utero, including miscarriage, low birth weight, and abnormalities in skeletal and reproductive system development.
How To Find Out If Your Water Contains Chromium-6
If you live in the continental U.S. you can find out if elevated chromium levels are present in tap water in your area by visiting EWG’s interactive map.
If you have a private well, it is a good idea to have your water tested regularly by an independent lab. Since some indoor plumbing fixtures have been found to leach hexavalent chromium into drinking water, it is best to have your water tested at the tap.
Canadian water utilities are required to inform their customers immediately if regular water monitoring indicates that chromium levels have exceeded .05 mg/L (about 50 parts per billion).
Keep in mind that this amount refers to total chromium, not just chromium-6. However, since this is quite a lot more than many scientists consider acceptable, concerned Canadians may also wish to have their water tested.
How to Protect Your Family
The simplest way to deal with high levels of chromium in your drinking water is to filter your home’s water. “Many people opt for a whole house filtration system to reduce heavy metals like lead and mercury, chlorine, pharmaceuticals, and organic chemicals like pesticides, herbicides, and VOC’s from their tap water,” says Kate Kyle, Marketing Director at Aquasana.
For additional protection, she also recommends installing an NSF-certified reverse osmosis filter at the kitchen sink to remove any substances that may make it past the initial filter, such as fluoride, chromium-6, mercury, arsenic, Radium, and Barium.
In reverse osmosis, water gets pushed through a semipermeable membrane which filters out particles of heavy metals and other contaminants. The result is pure, safe drinking water. However, a reverse osmosis system will also filter out beneficial minerals.
Since drinking water is an important source of minerals for many people, you might want to consider remineralizing your drinking water after it has gone through the reverse osmosis process.
You can do this by adding mineral tablets or small amounts of natural mineralizers such as Celtic or Himalayan salt or Pascalite clay to your water.
Safe Water Filtration Options
A reverse osmosis water filtration system can be expensive, depending on size and model. While this can be a cost-effective option in the long run (especially considering the health benefits for your family), the upfront cost may be prohibitive to some families.
Many people turn to bottled water as a temporary solution. However, this approach should be used with caution. Bottled water companies are required to meet the same standards as public water utilities, but they’re not required to publicly announce their findings.
A Natural Resources Defense Council study found that 22% of bottled water brands tested contained chemical contaminants exceeding levels allowed by the state.
Bottled water also is typically not tested nearly as often for biological contaminants, as evidenced by a recall of 14 brands of bottled water for E. coli contamination.
Finally, bottled water brings with it a heavy environmental toll, and in the long run it is much more expensive per glass.
A better solution for those who need to watch their budget, or for renters who do not wish to install a permanent filter, is a countertop filter or a pitcher filter. These standalone units are typically less expensive than reverse osmosis and are completely portable.
Here are our top three recommendations for home water filtration:
BOROUX
BOROUX filtration systems are designed with sustainability and safety in mind. Their filters effectively reduce harmful contaminants, including:
- Chromium-6
- Lead
- Arsenic
- Chlorine
- Fluoride
- Pesticides
- Heavy metals
- Because of the concerns with fluoride in drinking water, we chose to add the fluoride filters to our system.
AquaTru
AquaTru uses advanced reverse osmosis technology to provide ultra-pure water. Their countertop systems are NSF-certified to remove:
- Chromium-6
- Lead
- Arsenic
- Fluoride
- Nitrates
- PFAS (Forever Chemicals)
- Chlorine and chloramines
- VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
Clearly Filtered
Clearly Filtered uses advanced Affinity Filtration technology to target more than 365 contaminants while preserving essential minerals. Their water filters reduce or eliminate:
- Chromium-6
- Lead
- Fluoride
- PFAS (Forever Chemicals)
- Chlorine and chloramines
- Pesticides and herbicides
- Microplastics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Heavy metals (e.g., mercury, arsenic, cadmium)
- VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
ZeroWater
ZeroWater’s filtration pitchers and dispensers utilize a 5-stage ion exchange process to provide clean, great-tasting water. They reduce or eliminate:
- Chromium-6
- Lead
- Chlorine and chloramines
- Fluoride
- Mercury
- Aluminum
- Pharmaceuticals
Regardless of which water filtration system you choose, be sure to ask for a performance data sheet before investing. This document should be available from the manufacturer and will identify any third-party testing of the unit along with a list of contaminants it was found to remove to an acceptable standard.